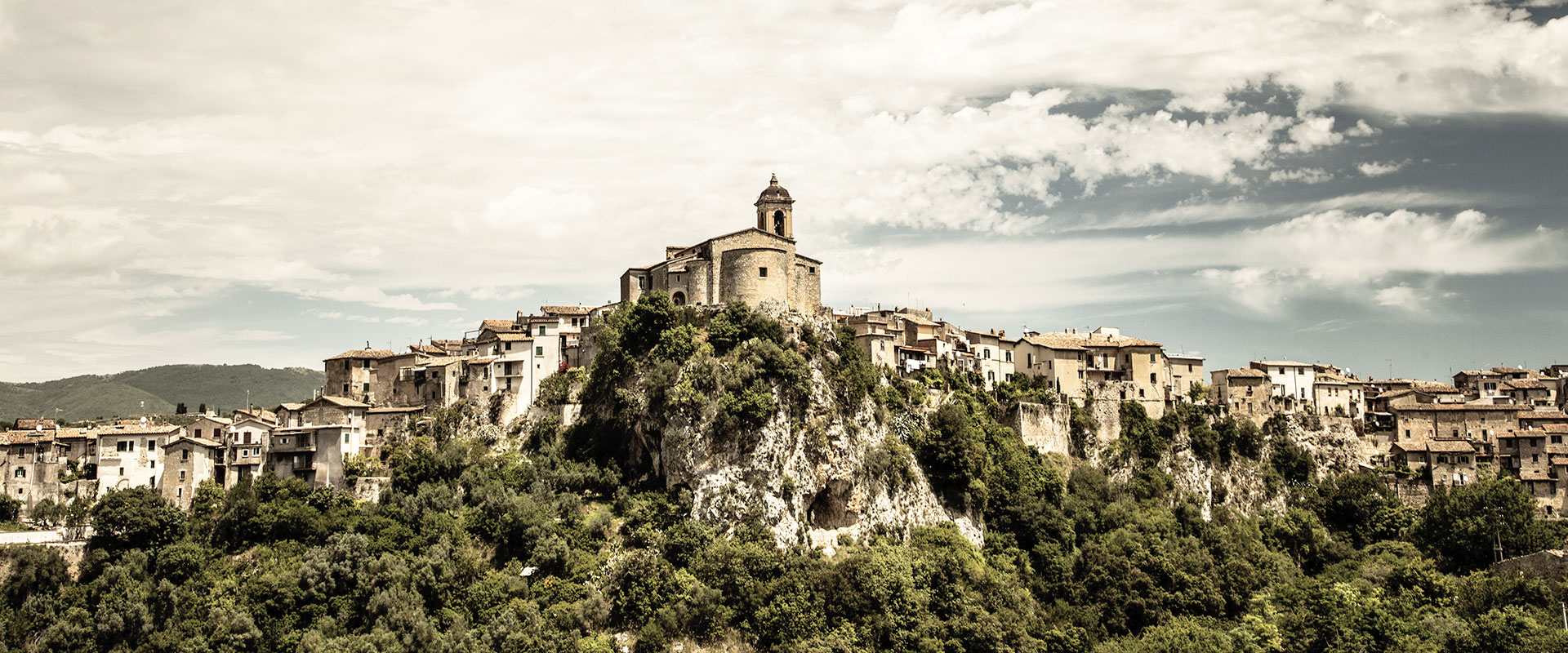
Toffia
![]() Population: 933 ( 460 M. – 473 F.)
Population: 933 ( 460 M. – 473 F.)
![]() Altitude: (s.l.m.) 262 m
Altitude: (s.l.m.) 262 m
 Distance from Rome: 57,9 km.
Distance from Rome: 57,9 km.
![]() Distance from Rieti: 40,5 km.
Distance from Rieti: 40,5 km.
Numerous findings testify today the human presence in the territory of Toffia since the Middle Bronze Age (1700-1350 BC).
The Roman period, as easily stated by the remains almost completely buried in a rustic villa in Marignano (villa Marianus or Marinianus) testify that Toffia was inhabited between the first and second century. A.D., and the from numerous archaeological fragments found in the country we can assume that Toffia was an important center even then.
The first documented evidence of a portion of this area is shown in the Farfense Summary of Gregorio da Catino to record a deed of gift, and dates back to before the coronation of Charlemagne, when in 761 the so called Aliperto Sundebado gives the Monastery of Farfa all its assets placed in the Criptula (today Grottuccia).
A Notitia Judicati (Lombard judgment) of 940, attests that in Castellum de Tophila near Aecclesiam Sancti Laurentii Leone recognizes the Farfa Abbey ownership for half of the castle and town still recognizable today: Casalis Meianula et Criptulae et Curiano.
Donations to the Church were very popular in the Middle Ages and were motivated by the desire to ensure the remission of sins after death, but also by a prudent administrative calculation: in the unstable political and social conditions of that time you took away the properties to the dangers of expropriation wars and devastation, putting them safe in the hands of the Church and reserving the usufruct for themselves and their heirs. Sometimes, however, even this solution was not enough for guaranteeing it, as evidenced by a 1116 document where the Farfa monks calling for justice to Pope Paschal II to the usurpations suffered in their possessions, and among them we find Criptulae et Tofiam Castellum.
The original castle, at the todays’s Via Castel di Dentro, in the fourteenth century saw a remarkable importance, being the second seat of the Bishop of Sabina. The population growth resulted in new buildings and in the late fifteenth century this area was reorganized with the construction of a fortress, the expansion of the walls and a new door, the Major Dorr (Porta Maggiore).
During the period in which the Orsini ruled at Farfa, Toffia was also under the control of the baronial family, but in the sixteenth century at the end of their hegemony, the castle returned to full possession of Farfa monastery and shared its fate.
Video
Phone Numbers
MUNICIPAL OFFICIES
Indirizzo: Via Porta Maggiore, 9
Telefono :0765 326032
Fax :0765 326375
Indirizzo email: [email protected]
Indirizzo PEC: [email protected]
Sito web: www.comune.toffia.ri.it












